Turbugan: An Adversarial Learning Approach to Spatially-Varying Multiframe Blind Deconvolution with Applications to Imaging Through Turbulence
IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory — 2022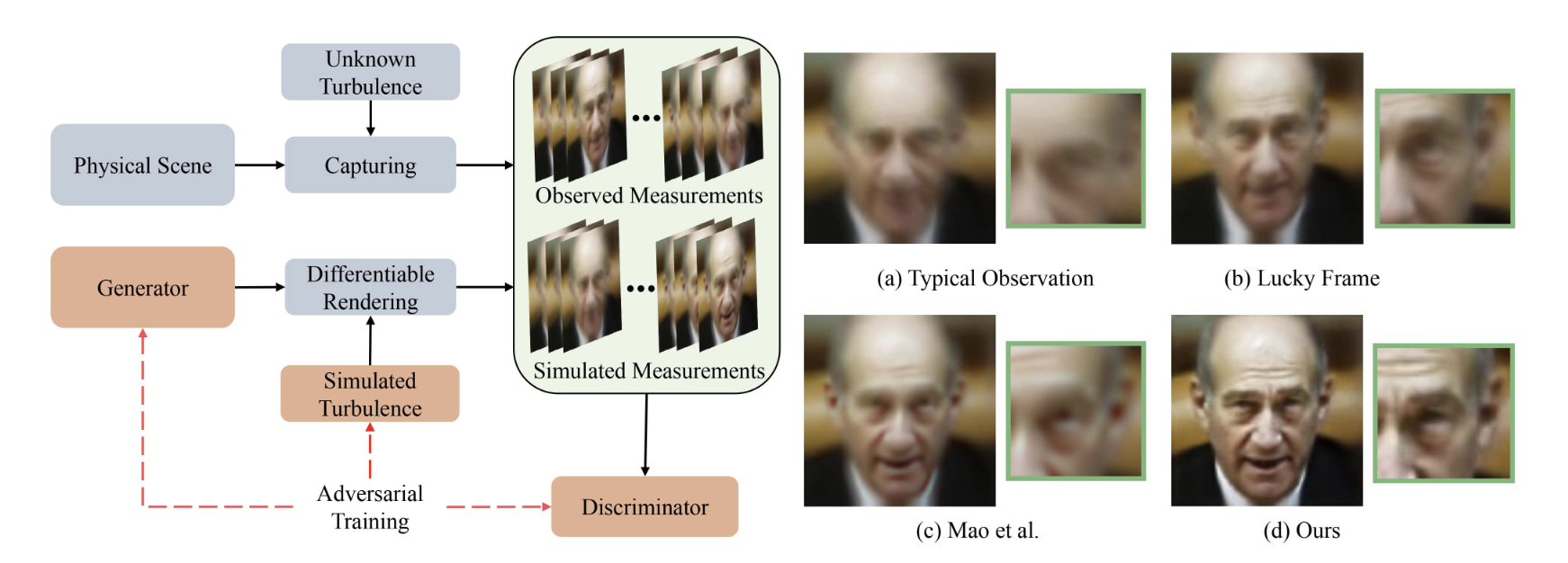
We present a self-supervised and self-calibrating multi-shot approach to imaging through atmospheric turbulence, called TurbuGAN. Our approach requires no paired training data, adapts itself to the distribution of the turbulence, leverages domain-specific data priors, and can generalize from tens to thousands of measurements. We achieve such functionality through an adversarial sensing framework adapted from CryoGAN, which uses a discriminator network to match the distributions of captured and simulated measurements. Our framework builds on CryoGAN by (1) generalizing the forward measurement model to incorporate physically accurate and computationally efficient models for light propagation through anisoplanatic turbulence, (2) enabling adaptation to slightly misspecified forward models, and (3) leveraging domain-specific prior knowledge using pretrained generative networks, when available. We validate TurbuGAN on both computationally simulated and experimentally captured images distorted with anisoplanatic turbulence.
@article{ Feng2022Turbugan,
author = { Feng, Brandon Y. and Xie, Mingyang and Metzler, Christopher A. },
title = { Turbugan: An Adversarial Learning Approach to Spatially-Varying Multiframe Blind Deconvolution with Applications to Imaging Through Turbulence },
journal = { IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Information Theory },
year = { 2022 },
}